Hadoop & MapReduce with AWS Elastic Map Reduce (EMR)
What is Hadoop?
Hadoop is an open source platform that expedites the processing & analysis of large data (both structured and unstructured) in a distributed computing environment. Hadoop is comprised of two fundamental components:
- Distributed File System: This is the file structure of Hadoop that is set across several computer nodes (datanodes, slave nodes) to help process large amounts of data. The hdfs can be accessed by several different clients as if they were one local client.
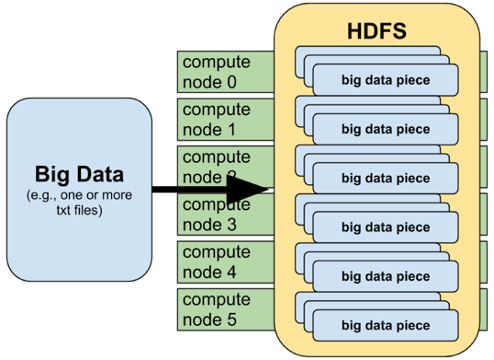
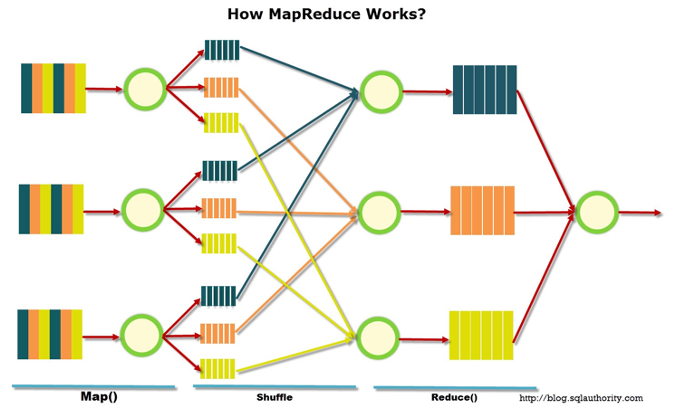
- MapReduce: This algorithm allows for queries to be processed in parallel as opposed to the traditional serial fashion through distributed applications. The map function will take a function and apply it to each subsequent value in the dataset. The reduce function then takes the separate data nodes (master/slave relationship) that will process an individual query and process results in tandem. These key value pairs are then aggregated together and returned to the name node.
What is Hive?
Apache Hive is a querying language (HQL) that works on top of the Hadoop platform to perform data querying and analysis. Hive is a framework for MapReduce, automating the process.
Building a Hadoop Cluster with AWS & EMR
Built using the following tutorial
Amazon Elastic Map Reduce (EMR) on Amazon Web Services (AWS) allows for simplified node clustering and services for Hadoop. EMR is a scalable managed framework that automates the process of node provisioning, and both cluster and Hadoop configurations. It is all managed through the AWS dashboards, and requires little technical knowledge to get started. EMR consists of clusters:
- Master Node: In charge of running software and procedures to coordinate the data analysis. This is the main node for interactions.
- Task & Core (Slave) Nodes: run tasks as directed by the master node, which can access the Hadoop Datafile System (hdfs). The queries ran on these nodes are aggregated and returned to one output directory on the hdfs, accessible by the master node.
S3 Sample Data & Buckets
S3 is Amazon’s cloud object storage capability and allows users to store objects, data and meta data. The first step is to insatiate an S3 account and create a bucket. A bucket is a unit of storage in AWS and will serve as the location of the hdfs for this example. 
Within this bucket – create two folders for “logs” and “output”. The output folder is where the results from the MapReduce function will be stored on the hdfs. 
Create AWS Key Pair
AWS provides key pairs that allow for password-less secure connections to services and nodesthrough Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol. If using the bash terminal to SSH into remote machines, this key pair can be downloaded and used for password-less entry into node clusters. It is important that you do not lose access to this key pair, or else you will lose access to the nodes as well. 
Create a Cluster
EMR allows for simple generation of a cluster (distributed computing consisting of master nodes and slave nodes) to execute data querying. 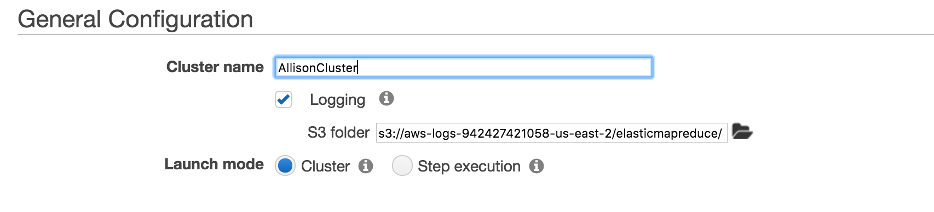
When selecting the software that we want to have installed and configured on the node instances select Hadoop and Hive. Selecting this option is akin to installing these programs and applications on the instance – but without the hassle of configuration and installation woes. 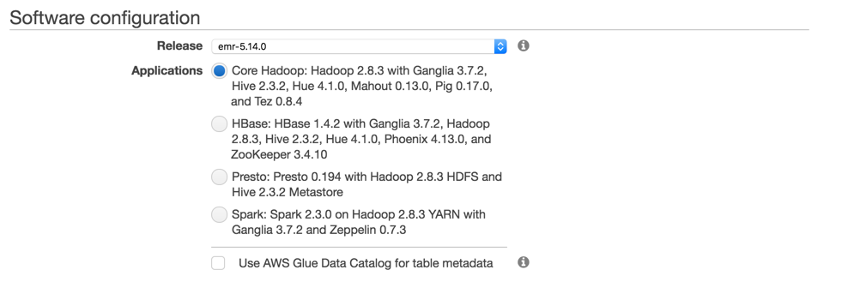
Hardware configuration within the cluster will determine the number of nodes to generate. Instead of creating two instances individually within AWS, this will automatically generate 1 namenode (master) and 2 core (slave) nodes. 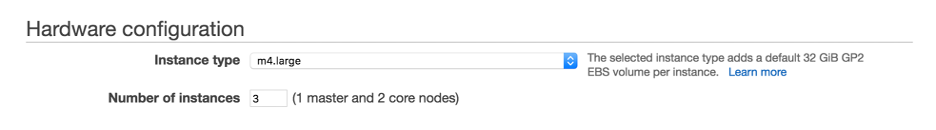
The final step is to configure security and access, which we can do with the previously generated key pair of “allison-key.pem”. 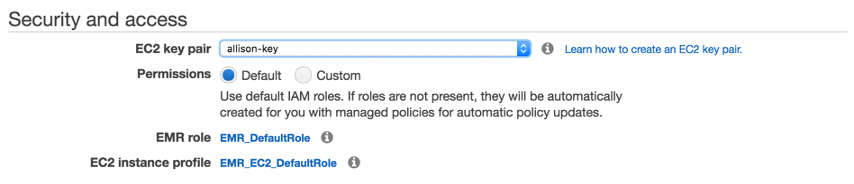
After launching, the cluster can be seen in the EMR dashboard. We can see the 1 Running master node and the 2 running Core nodes. 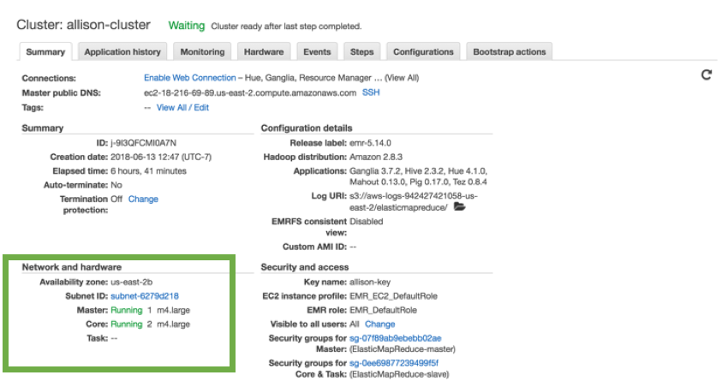
To see these core instances that have been created, the EC2 Dashboard shows the 3 generated instances. Two of these instances have been created as the slave nodes and one as the master node, as shown with the security group and the functionality that is permitted on each node. 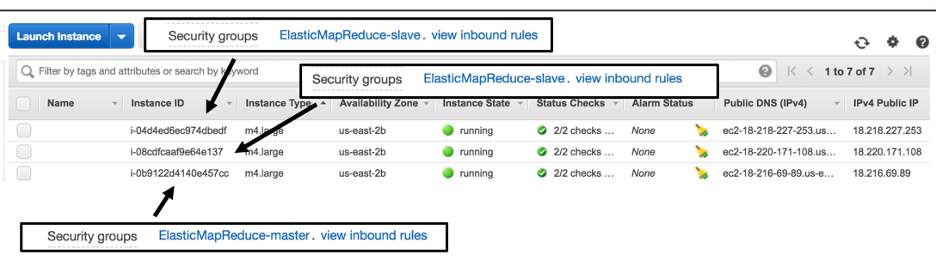
Data Setup
AWS provides access to several sample datasets and for this example we are using the data provided in Amazon CloudFront Logs. The expected output from this example script will be two pieces: Total Requests per Operating System.
Hive Script Configuration
To add the Hive script accessing the data referenced above a Step needs to be added to the EMR cluster. A step is a “distinct unit of work, comprising one or more Hadoop jobs that run only on the master node of an Amazon EMR cluster” source. The step added will run a prewritten Hive script to query the CloudFront logs. The output for this Hive step is stored in the output folder that was created in the S3 Bucket. This step will automatically run once the node cluster has started.
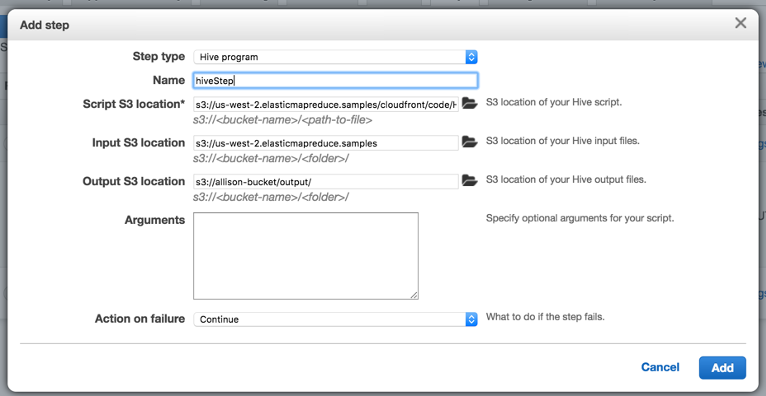
Congratulations, you have Hadoop’d!
To validate that the step ran the “Application history” tab will provide history of the services ran on the node cluster. The hive job shows as “Succeeded”. 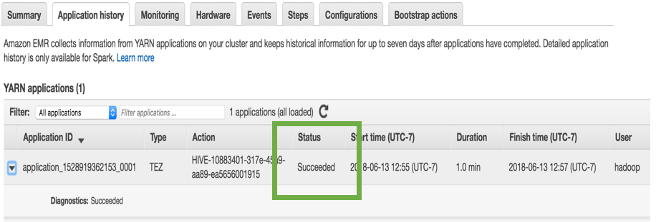
Additionally, the “Events” tab acts as a log for each action taken on the Node cluster. 
The output of the Hive script is stored in the output folder of the S3 bucket. 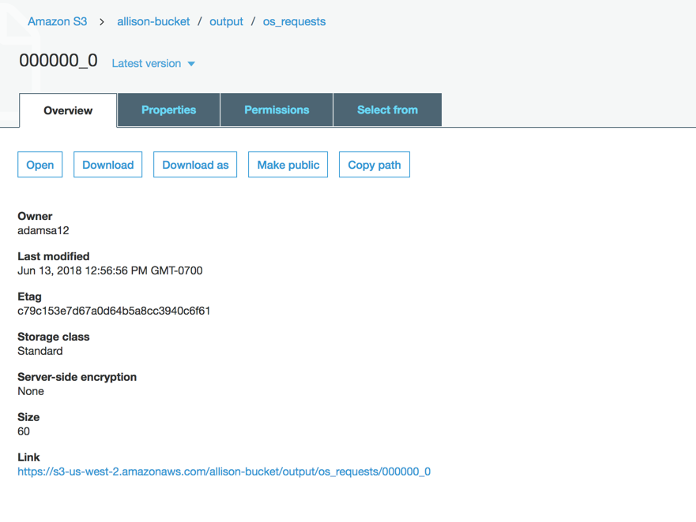
After downloading the file, you can see the successful query of the Total requests per Operating System. 
